
Smart Solar Panel
Why use Solar Energy
Solar energy is gaining popularity in India & is becoming more affordable & easier to generate than ever. People like you are looking for more ways to be energy smart with RE sources that help protect the environment. Solar energy is the one of the most effective sources of RE because of the reliable amount of sun the world gets. Ever-advancing tech’s that are emerging will continue to harness this source in better, easier & cheaper ways making solar the fastest growing RE source. Carbon footprint of solar PV panels is already quite small and, as the materials used in them are being increasingly recycled, it continues to shrink. Your electricity bills could decrease quite a bit because of the power you are generating & using, & not buying from your supplier. As solar panels are considered ‘permitted development’ you usually don't need a permit to install them on your roof. There are a few limitations you need to bear in mind before installation. Once installed, solar panels require very little maintenance. They are generally installed at an angle which allows rain to run off freely, washing dirt & dust away. As long as you keep them from becoming blocked by dirt, solar panels could last for over 25 years with little loss in efficiency. Investing in a solar power system makes you less reliant on the National Grid for your electricity. As an energy generator, you can enjoy cheaper electricity throughout the day. & if you invest in battery storage, you could carry on using solar energy after the sun goes down. You’ll be contributing to a more efficient way of generating energy. Transmitting energy from power plants across extensive networks to your home inevitably results in energy loss. When your power is coming direct from your rooftop, the loss is minimised, so less energy is wasted. The Feed in Tariff is a Govt. backed scheme offered by your electricity supplier and, if you opt for it, you could get paid for the energy generated by your solar PV system. Solar panels are generally good investment for your home. Current trends in the energy market mean that a home with solar panels could command a higher price in the future than one without. Smart solar is the advanced version of solar energy tech. Converting the solar energy into electrical or thermal with advanced management & efficient utilization is the new global smart solar market. With the increasing demand of energy worldwide, usage of alternative sources is increasing day by day & solar energy is the best evergreen energy option. That is the key development factor for advancement in smart solar energy solution market. Currently smart solar market is valued at $6.47 billion, & it is estimated to achieve $13.89 bn by 2022, at a CAGR of 16.8% during 2016-23.
Smart module market gaining momentum
These intelligent packages have grown from being just panels equipped with power optimizers. Today’s good smart modules involve any type of module-level electronics with functions like remote monitoring, module-level shutdown, voltage limiting, increasing power harvest & more. The way we think of smart modules is anything that has something built into it that does more than just sit there & generate power from the sun. Smart modules are something where it differentiates a module. In an industry where basic solar modules used to use bankability to differentiate, there’s more & more companies that claim that. This is a way to continue to innovate & be different from all the manufacturers out there. Power optimizers are still the dominant add-on for smart modules. With system owners demanding more from their PV systems & installers demanding more in terms of installation efficiency, module manufacturers can better satisfy the current market requirements by embedding power optimizers. There is an obvious price difference between traditional modules & the smart
Smart Solar PanelsSmart Solar PanelsSmart Solar PanelsSmart Solar Panels Smart Solar Panels Smart Solar Panels Smart Solar PanelsSmart Solar Panels Smart Solar Panels : Marketing Strategies : Marketing Strategies: Marketing Strategies: Marketing Strategies: Marketing Strategies: Marketing Strategies : Marketing Strategies : Marketing Strategies: Marketing Strategies
variety. With added monitoring & hardware comes added costs, & the potential for added import taxes. Many module manufacturers were paying import tariffs on their finished goods. Integrating power optimizers into the modules meant that they also had to pay tariffs on the power optimizer, thus raising the cost. This offsets the value of integration. Industry is starting to see more strategies from module manufacturers that limit the impact of the import tariff, meaning that these integrated products are starting to drive cost reduction for installers. There have also been some hiccups in relaying to end-users the real benefits smart modules can bring. People who thought solar couldn’t work on their houses because of huge oak trees casting shade now have real generation capability with smart modules. People will see that these technologies work, there will be a longer track record of increasing your energy production, a track record of them working properly.
It’s also likely that other industry requirements could spark the rise in smart module popularity. Now is an ideal time in the market for smart modules. Cost reduction for installer is a constant battle. Since integrated modules can reduce hardware costs & decrease installation times, they have potential to drive costs down. Also, smart modules also have the potential to create differentiation for module manufacturers in a highly commoditized & competitive market. An intersection of cost reduction & differentiation creates a highly attractive environment for smart modules going forward. This smart solar technology provides support, communication, distribution, monitoring & planning & enhanced integration systems. Such advancement in technology has led an increase in the demand for smart solar system. Deployment of solar solutions helps user to save electricity expenses, & increase the efficiency of solar components using monitoring & communication technique. Increasing rates of conventional electric energy & high consumption demand for more energy are the major factors driving the market growth. Also the awareness for natural energy solution is increasing, because people are showing their interest in alternatives for energy solution. Moreover govt. is creating policies & regulations to utilize the solar energy which is also driving the solar energy market. Only restraining factor is high cost of installation. Cost of solar panel itself is high. Adding other components for smart purpose makes system highly expensive. But this high cost will eventually cut down by more production & more deployments. Instability & inefficiency in system could be a challenge to the system. Solar energy system is developing in recent years; even economies of nations are increasing rapidly which could offer new opportunity to the solar industries.
Evolving solar industry & increasing environmental awareness coupled with technological evolution open major opportunities. Market size for smart solar segment has considerably grown over the past few years on the account of evolving solar industry & the emergence of technologies such as MDM, SCADA, remote metering have further augmented the opportunity areas for this market. Advancement in solar applications, platforms, services coupled with increasing integration of IoT with smart solar solutions has led to sig. investment in smart solar projects globally. Increasing env. awareness about solar industry amongst the public will also act as an opportunity for the smart solar market. High initial investment, inadequate financial incentives for utilities & reduction of solar subsidies in many countries are the major restraints of the overall growth of this market. Meter data management & network monitoring solutions segments are expected to be the most promising segments. Smart solar market has been segmented into solutions, services, applications, & industry sectors. Meter data management & network monitoring solution segment is projected to grow with a high growth rate; hence, will present good market opportunity during the forecast period. System integration & deployment services holds a major share in the smart solar services segment. Increasing integration of smart solar technologies with different industries is considered as the primary driver influencing the growth of the smart solar services market. Presently, North America contributes the maximum market share North America is expected to have the largest market share & would dominate the smart solar market from 2015-20, with growing no. of smart solar projects, increasing smart solar meter roll outs, & increasing grants & solar subsidies from the U.S. govt.. APAC & Middle East & Africa offers potential growth opportunities due to the developing large-scale infra, growing no. of smart city projects, & growing energy requirements. Major vendors covered in the smart solar market for this study include ABB Group, GE Power, Itron Inc., Schneider Electric, Siemens AG, Echelon Corporation, Landis+GYR AG, Sensus USA Inc., Silver Spring Networks, & Urban GreenEnergy Int’l. Smart solar market can be segmented on the basis of Solutions like asset mgt., network monitoring, meter data mgt., analytics, SCADA, remote metering, & outage mgt. Services like system integration & deployment, support & maintenance, consulting, & demand response services Applications like commercial & industrial, residential, Industry Sectors like govt., utilities, healthcare, construction, education, agriculture, others & Geography.
Marketing & the 4 P’s
We live in a society that bombards consumers with messages, from pop-ups on computers, to on-line chat room links, to e-newsletters & eblasts, to advertising in traditional media, all designed to build a “share of mind” for a product, service or social cause. Marketing is not merely communications. It is the sum presentation to the customer of a value equation that results in a sale or action. Marketing is the process of identifying what the consumer needs, how the product or service can address that need, how to communicate that value in a compelling way, & how to deliver that message in the most efficient & effective manner. When state solar incentive program managers think like marketers, they will sharpen the focus of outreach efforts & improve the effectiveness of their solar program offerings. The classic elements of marketing, the 4 P’s: Product, Price, Place, Promotion; offer a useful matrix to assess state solar programs. Solar program initiatives should address each of the 4 P’s. For example, a consumer will not buy a poorly manufactured product or one with a questionable reputation merely because the price is good. Similarly, the best quality product must be affordable to ensure market share. While state solar programs do not produce solar panels, price them, or control quality of technology or installation, their program success is integrally linked to success of solar suppliers. Both share the same goal: building a strong customer base for solar power in their region. Each plays an imp. part in marketing solar. However, state incentive programs define the 4 P’s in a slightly different way than do solar suppliers.
For marketing purposes, state programs can evaluate the Product from the perspective of consumers’ rational & emotional attitudes towards solar technology. These attitudes affect desire to purchase. Consumer reaction to solar tech (e.g., price, reliability, quality issues) informs marketing & communications approaches by identifying both the opportunities, the strengths & positive attributes that should be marshaled, & the barriers, the concerns & “issues” that prevent sales.
Price is one of the single biggest barriers to growing the solar marketplace; many states are addressing the financing of solar to help overcome consumer price concerns. Today, financing mechanisms are broadening access to solar power & making it available to new customer groups. However, states must ensure that prospective customers are aware of these new financing strategies & aggressively promote the financial “value” of solar products to consumer targets.
Place, or channels through which solar is sold, also is an area where solar programs have an imp. role through their work with installers, developers, & suppliers. Building a strong supplier network is critical in keeping up with rising demand; ensuring that customers can easily find an installer is part of this task. States also should look at how complex the solar sales process can be for consumers & how solar programs can minimize & ease the transaction process.
Promotion of solar should be a primary focus as state programs seek to increase visibility of solar installations & broaden the appeal of their solar incentive programs. Using communications & promotional strategies to favorably present solar in the marketplace & ensuring that the right messages are presented to the public will help build a stronger market for solar tech’s.
As solar incentive programs examine their program offerings through the lens of Product, Price, Place & Promotion, they may conclude that they need to better understand their customer through market research, focus their efforts on specific target customer bases (customer segmentation), & address key messages to reach those audiences effectively & efficiently (communications). This evaluation process informs the elements of a solar marketing plan. Whether a marketer’s goal is to persuade a customer to visit a store, sample a new product, purchase an existing product, visit a website, make a donation to a nonprofit org., or inquire about a solar incentive program, the process is the same. In essence, marketing matches the right customer to the right product, resulting in a sale. As states apply marketing approaches to their solar initiatives, they will become more customer-focused, rather than program-focused, and, as a result, become more effective in achieving solar goals. If one starts with the end in mind, a solar marketing plan identifies how a state program will achieve installed megawatt goals through acquisition of residential, commercial & institutional customers. 4P’s ensure that all aspects of the sale are covered. Improving process of purchasing solar will not alone make a difference in overall sales if the price/value equation has not been addressed. If consumers are not confident about reliability of solar, improved pricing alone will not matter. All elements must work together to motivate target customer to take action. Hence, the dev. of a solar marketing plan must start with consumer in mind.
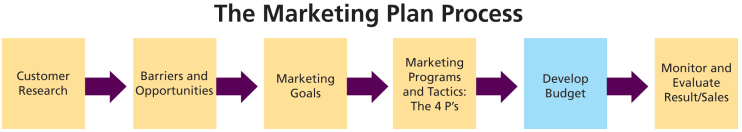
Developing a Marketing Plan - How to Begin
Marketing is a problem solving activity. Finding & understanding what problems require solving is the first & most imp. step in constructing an effective marketing plan. Thinking like a retailer is key because it will ensure that programs & initiatives, as well as communications & promotions, are designed to create a call to action & move customers towards the sales process. A marketing plan is a living, breathing document that guides activities over a period of usually no more than one to two years & is focused on achieving quantifiable & measurable goals, such as megawatts of installed solar. Activities within the plan must address core customer segments that are imp. to the solar program, such as low-income housing, schools & institutions, large commercial customers, & installers. The process of developing an effective plan includes the following steps. Market analysis begin by assessing past successes & failures. Identify what has worked & what has not. Which customer bases are responding & which are underdelivering? Are there geographic issues to be addressed within your plan? Customer Research If there are questions about the motivations & attitudes that core customer groups have about solar power, a customer research project & market analysis will identify the opportunities & barriers that must be addressed in the marketing plan. Solar programs may want to rely on an outside resource such as an advertising agency or marketing consulting group to help with this aspect of the plan. Establish Marketing Objectives What will the marketing plan accomplish? What are the goals? A marketing objective might include a percentage increase or megawatt goal for specific customer segments, such as commercial & industrial, residential, or institutional solar installations. Marketing Strategies How will the solar program reach its objectives? This report suggests that Cost, Reliability, Complexity, Inertia & Message all must be addressed in an effective marketing plan. There may be other strategies relevant to your specific market that should be included or receive priority. A marketing strategy that addresses value, for example, might include offering financial tools that reduce the high out-of-pocket costs for solar installations. A marketing strategy to address reliability may include raising visibility of solar in the marketplace. Implementation Tactics are the specific programs & initiatives that address the marketing strategy. The examples cited in this report from solar stakeholders across the country are examples of marketing tactics. The rest of the marketing plan includes a budget & timeline, as well as an approach to evaluate the success of specific tactics. There may be other resource needs required by the solar program. All key stakeholders across the org. should review the marketing plan while in development to ensure that it is addressing the right issues & to ensure buy-in. It is also critical that implementation challenges be coordinated with appropriate personnel to ensure that adequate resources & timeframes are accounted for.
Conclusion
Effective marketing guides how, when, & where product information is presented to consumers, with the ultimate goal of persuading consumers to purchase solar energy systems. Therefore, state solar program managers must view themselves as a critical part of the solar sales process. Understanding what problems need solving & how best to address them is at the heart of the Solar Marketing Plan. Messages that connect on a financial or value level are most likely to succeed. There are e.g’s of effective solar marketing activities all over the country to draw upon. As solar programs begin to think like marketers, they can assess “how they’re doing” by asking a series of questions to determine whether solar marketing efforts are on the right track, including: How are new customers learning about solar? Should we do more to help? Where are our best opportunities? Are we providing consumers with valueoriented financial offerings that make solar more affordable? Are consumers aware of the new financial approaches that we offer? Are we adequately promoting the value & affordability of solar? Is it prominently displayed on our website? Are we targeting the right audiences in our market to achieve our objectives? Have we left any core audiences untouched? Do we understand the consumer barriers to purchasing solar that are specific to our market? Should we initiate research to advance our understanding & the effectiveness of our activities? Have we done an inventory of communications materials to ensure that we are speaking with one voice, promoting one brand, & hitting the right messages? Are there NGO’s & other stakeholders in our market that we should be aligning with to advance our goals & leverage our investment? How do we overcome inertia & help push interested customers to act? How do we create more visibility for solar in our market? Are there high visibility locations, personalities or opportunities that will increase penetration? Do we have a sufficient group of installers in place? Will we need more? How can we attract them? Do realtors understand the value of solar & know how to speak about it effectively? Is there a role for traditional & new media in our marketing mix to build awareness? Are there innovative ways to utilize earned media beyond press releases & ribbon cuttings to increase interest in solar? Are there other solar partners (utilities, trades, chambers, cities & towns, sports venues, etc) that we should be working with to increase interest in solar power? Are we cross promoting energy efficiency & solar energy to maximize interest in both? Are we creating a database of consumers & are we using that database effectively? As states increasingly compete with each other for green jobs & clean economies, being savvy solar marketers becomes more imp. than ever. By asking these questions, & by creating a plan that provides a comprehensive approach to solar marketing, solar programs will maximize their investment in solar incentives, & expand customer base for solar energy throughout their markets.











leave your comment